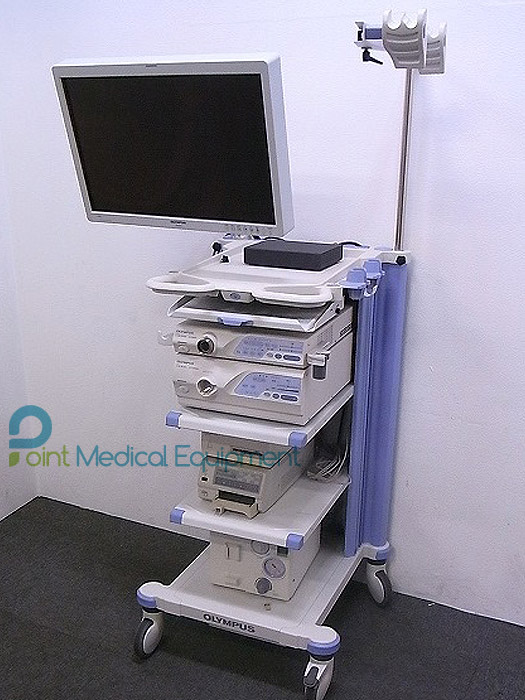







* Lamp usage time: 35h
* Voltage: AC 100V
* excellent condition.
Addition to the normal light observation, it is EVIS LUCERA SPECTRUM system also corresponding to the NBI observation.
Depending on the combination of the video scope, AFI, also IRI of various observation is possible.
EVIS LUCERA SPECTRUM endoscopic video imaging system for observation using specific light spectra
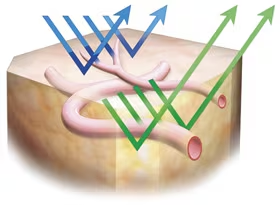
Aiming to assist the early detection of minute lesions such as cancer and preoperative accurate diagnosis of diseased areas, this new system delivers enhanced images of characteristic changes of lesions - capillary vessels in the mucosal surface, and slight thickening of the mucosa as well as vessels deep in the mucosa - by controlling the wavelength of light used. The system incorporates three imaging functions using specific light spectra addition to normal light imaging with High-resolution HDTV. The three types of imaging are: Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) for enhancing capillary vessels in the mucosal surface and minute mucosal texture, Auto Fluorescence Imaging (AFI) for enhancing tumorous lesions and normal mucosa in different colors, and Infra Red Imaging (IRI) for enhancing vessels deep in the mucosa and information about the blood flow through them. NBI can be used simply by connecting it to an existing Olympus videoscope*1, while AFI and IRI will require a dedicated videoscope*2 (marketing approval application under review in Japan).
Background of Olympus Evis Lucera Spectrum Endoscopy
In recent years in Japan, in parallel with aging of the population, mortality from cancer is tending to increase, particularly due to colon and rectal cancers. In contrast, the mortality rate of gastric cancer is decreasing, thanks to advances in medical technologies including the development of endoscopes and early diagnosis and treatment. According to the Survey of Medical Care Activities in Public Health Insurance in fiscal 2004 published by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare, the number of endoscopic examinations of the stomach and duodenum increased by 16% and that of colon (ascending colon and appendix) by 46% from fiscal 2000, so the use of endoscopes is expected to continue to spread as essential diagnostic and therapeutic instruments for screening (for detecting pathological changes), precise examination, and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases. Furthermore, following the revision of medical treatment fees in fiscal 2006, Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of early-stage malignant tumors, which involves extensive endoscopic dissection of the lesion, became covered by medical insurance. This requires a next-generation endoscope allowing more precise diagnosis, and preoperative confirmation of the lesion areas and area to be dissected in particular.
Olympus has therefore developed LUCERA SPECTRUM, aiming to assist the early detection of minute lesions such as cancer and preoperative accurate diagnosis of diseased areas. To help physicians make precise and accurate diagnoses, Olympus has been developing a number of image processing techniques including the HDTV-Compatible Endoscope launched in 2002, adaptive IHb color enhancement*4, and structure enhancement*5, and these have built up a high reputation in the market. Based on our know-how in observing the mucosal surface under normal light by using image processing techniques, we have successfully developed a new diagnostic tool: an endoscope that optically depicts enhanced images of characteristic lesions in the superficial and deep layers of the mucosa by using specific light spectra for imaging. The new LUCERA SPECTRUM enables Olympus to support the full range of endoscopic procedure from screening to precise examination, thus helping to improve patients’ QOL. Olympus aims to make imaging using specific light spectra as the de facto standard for next generation endoscopic systems.
Main features
<Supports the early detection of minute lesions by three types of special illumination imaging , and supports endoscopic treatment and preoperative diagnosis for surgical treatment>
LUCERA SPECTRUM offers three types of special illumination imaging (Narrow Band Imaging, Auto Fluorescence Imaging, and Infra Red Imaging) to display enhanced images of characteristic changes of lesions – including capillary vessels in the mucosal surface, a slight thickening of the mucosa, and veins deep in the mucosa – by controlling the light wavelength. The viewing mode can be switched from normal light imaging to specific light imaging at the touch of a front panel for rapid, simple examination, placing less stress on both the physician and patient.
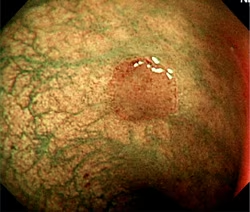
 1.Narrow Band Imaging = NBI
1.Narrow Band Imaging = NBI
NBI displays enhanced images of capillaries in the mucosal surface and detailed mucosal texture by irradiating two narrow wave bands (390–445 nm/530–550 nm) which are strongly absorbed by circulating hemoglobin. If signal processing is performed using a pseudo-narrow band image, the state of mucosa tissues and observation conditions influence the results and good effects cannot be obtained. However, with NBI, the wavelength of the irradiating light itself is altered, and capillaries in the mucosal surface and detailed mucosal texture can thus be processed effectively and stably. NBI is compatible with existing Olympus videoscopes.
Potential applications
NBI has been investigated in examinations of the hypopharynx, esophagus, colon, stomach and various other areas, and many papers on its applications have been published in journals and scientific meetings.
| Areas of application | Potential applications |
| Hypopharynx, esophagus | Identification of lesion area and benign/malignant diagnosis in hypopharynx cancer, early-stage esophageal cancer, Barrett’s esophagus*6 |
| Colon | Detection of minute polyps, malignancy diagnosis through pit pattern (gland duct structure) observation by combination with close-up/magnifying observation |
| Stomach | Diagnosis of histological type of cancer |
*6 Abnormal change in the esophageal lining to the columnar cell type normally found in the stomach lining as a result of inflammation of the esophageal lining caused by chronic gastric acid reflux.
 |
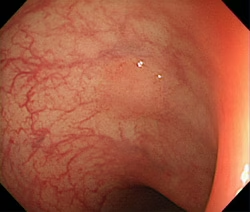 |
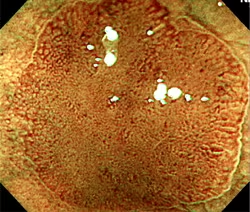 |
(Pictures by Dr. Yasushi Sano, Division of Digestive Endoscopy and Gastrointestinal Oncology, National Cancer Center, East Hospital)
2. Auto Fluorescence Imaging = AFI
AFI is a technology to display enhanced images of tumorous and normal mucosa with a different color by irradiating excitation light (390–470 nm) to observe auto fluorescence emitted from fluorescent substances such as collagen and light of wavelength 540–560 nm that is absorbed by circulating hemoglobin. Auto fluorescence is an extremely weak light that conventional CCDs can barely detect, and so optical fiberscopes have typically been used for observation. Combined with a dedicated videoscope (marketing approval application under review in Japan ) incorporating a high-sensitivity CCD that Olympus aims to launch within this fiscal year, even finer imaging quality will become possible.
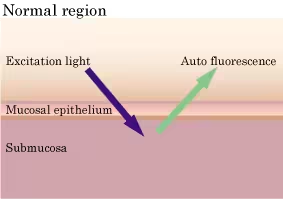 |
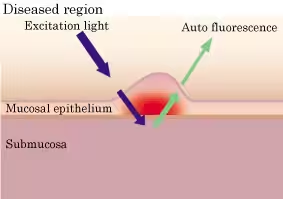 |
Potential applications
AFI has been investigated in examinations of the bronchi, esophagus, stomach, colon and various other areas, and many papers on its applications have been published in journals and scientific meetings.
| Areas of application | Potential applications |
| Bronchi | Detection of squamous cell cancer and premalignant lesion |
| Esophagus | Detection of early-stage esophageal cancer and premalignant lesion in Barrett’s esophagus |
| Stomach | Detection of accessory lesions*7 in gastric cancer, diagnosis of dissemination of the lesion |
| Colon | Identification of tumorous lesions in the colon |
*7 In gastric cancer the incidence of simultaneous multiple cancer is thought to be about 10% in the perigastric region.
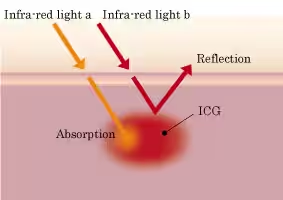
3. Infra Red Imaging = IRI
IRI is a technology to display enhanced images of the vessels deep in the mucosa and information about the blood flow through them which is difficult to recognize with the human eye, by irradiating light in two infra-red wave bands (790–820 nm/905–970 nm) following intravenous injection of ICG (indocyanine green)*8 which strongly absorbs the infra-red light. IRI is made possible by combining with the dedicated videoscope(marketing approval application under review in Japan)that Olympus aims to launch within this fiscal year.
*8 Color pigment that binds to blood proteins and is mainly used in liver function tests.
Potential applications
IRI has been investigated in examinations of the stomach, esophagus areas, and many papers on its applications have been published in journals and scientific meetings
| Areas of application | Potential applications |
| Stomach | Diagnosis of cancer depth and assessment for therapeutic measures. Differential diagnosis between cancer and adenoma (precancerous lesions). Foreseeing the volume of hemorrhage and measures for arresting hemorrhage following ESD (endoscopic submucosal dissection) |
| Esophagus | During esophageal variceal sclerotherapy, observing directly and dynamically/statically the distribution of curative agent over the esophagus and gastric lining |
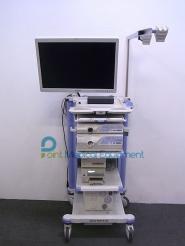
Main Specifications
| [EVIS LUCERA VIDEO SYSTEM CENTER OLYMPUS CV-260SL]*9 | |
| External dimensions | 382 (W) × 78 (H) × 498 (D) mm |
| Weight | 9.4kg |
| Power consumption | 150VA |
| Video signal output | HDTV (RGB: 1 or YPrPb: 1), SDTV (RGB: 3, Y/C: 2, NTSC: 2) |
| Main functions | Observation using specific light (Narrow Band Imaging: NBI, Auto Fluorescence Imaging: AFI, and Infra Red Imaging: IRI), HDTV output, adaptive IHb color enhancement, IHb pseudo-color display, structure enhancement, electronic zoom, color drift correction for live images, flash release, automatic iris control, pre-freeze image capture, automatic white balance |
| [EVIS LUCERA XENON LIGHT SOURCE OLYMPUS CLV-260SL]*9 | |
| External dimensions | 381 (W) × 162 (H) × 536 (D) mm |
| Weight | 16kg |
| Power consumption | 500VA |
| Lamp | Xenon 300W |
| Main functions | Observation using specific light (Narrow Band Imaging: NBI, Auto Fluorescence Imaging: AFI, and Infra Red Imaging: IRI), automatic 8-level automatic brightness control, adjustable aeration (high/medium/low settings), emergency lamp cut-ff |